April, 8th 2021
BACTERIUM
1) Chiefly round, spiral, or rod-shaped single-celled prokaryotic microorganisms that typically live in soil, water, organic matter, or the bodies of plants and animals.
2) They make their own food especially from sunlight or are saprophytic or parasitic.
3) They are often motile by means of flagella, reproduce especially by binary fission, and include many important pathogens.
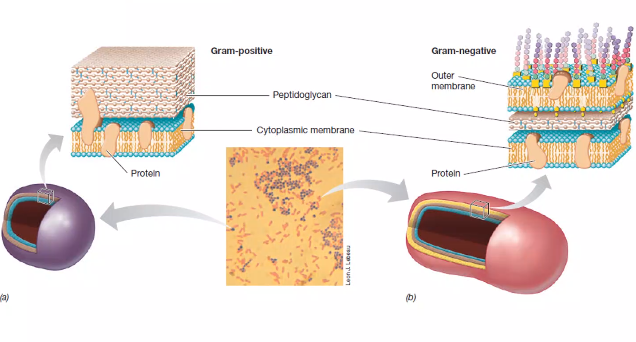
4) Bacteria lack a nuclear membrane or membrane-bound organelles and are categorized as gram-positive or gram-negative when a cell wall is present.
5) While many bacteria are aerobic requiring the presence of oxygen to survive, others are anaerobic and are able to survive only in the absence of oxygen.
CELL PROPERTIES
1) Metabolism: A cell is a compartment that takes up nutrients from the environment transforms them and releases wastes into the environment. The cell is thus an open system.
2) Growth: Chemicals from the environment are turned into new cells under the genetic direction of preexisting cells.
3) Evolution: Cells contain genes and evolve to display new biological properties. Phylogenetic relationships between cells.
4) Mobility: Some cells are capable of self-propulsion
5) Differentation: Some cells can form new cell structures such as a spore usally as part of a cellular life cycle.
6) Communication: Many cells communicate or interact by means of chemicals that are released or taken up.
ENERGY PRODUCTION
1) All cells require carbon as a major nutrient.
2) Heterotrophs: Requires one or more organic compounds.
3) Autotrophs: If the C source is CO2
4) Chemoorganotrophs: They use organic chemical compounds (glucose, acetate, etc.).
5) Chemolithotrophs: They use inorganic chemical compounds (H2, H2S, etc).
KIND OF MICROORGANISMS ACCORDING TO THEIR BEHAVIOR WITH OXYGEN
1) Aerobic obligates: Grow in normal oxygen tensions (21% air)
2) Microaerophilic: They are aerobes that grow in low oxygen tensions (2-10%).
3) Strict anaerobic: Cannot live in the presence of oxygen.
4) Aerotolerant anaerobes: They can believe both in the presence and absence of oxygen.
5) Facultative anaerobes: They do not need oxygen to grow but grow better in its presence.
PHYLOGENETIC TREE OF THE BACTERIAL DOMAIN
CELL MORPHOLOGY
1)Morphology refers to the shape of an organism.
2) Cocos: Bacteria with spherical or ovoid shape. Streptococci (chains) staphylococci (cluster).
3) Bacilos: Cylinder-shaped bacteria.
4) Espirilos: Some bacilli are curved in the form of a spiral.
3) Espiroquetas: Corkscrew-shaped bacteria.
3) Bacterias con apendices: Bacteria with stems and hyphae.
3) Bacterias filamentosas: Long, thin cells or chains of cells.
CELL WALL
1) Peptidoglicano: Rigid layer responsible for the resistance of the cell wall.
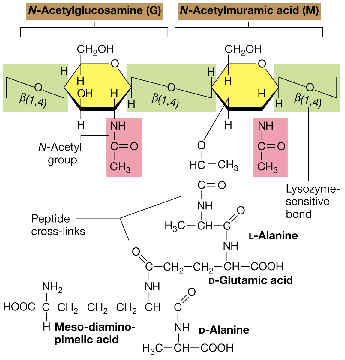
2) GRAM POSITIVES and GRAM NEGATIVES