1. The circular DNA double helix binds to the plasma membrane at one point.
2. DNA replicates and two double helices bind to the plasma membrane in close proximity to each other.
3. A plasma membrane is added between the junction points and they move away from each other.
4. The plasma membrane grows inward in half of the cells.
5. Mother cell divides into two cells.
Junction sites, Circular DNA
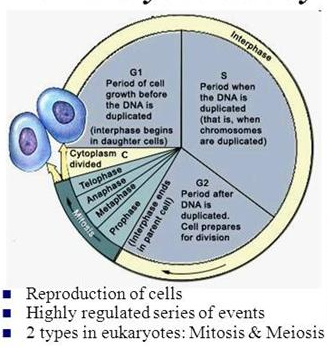
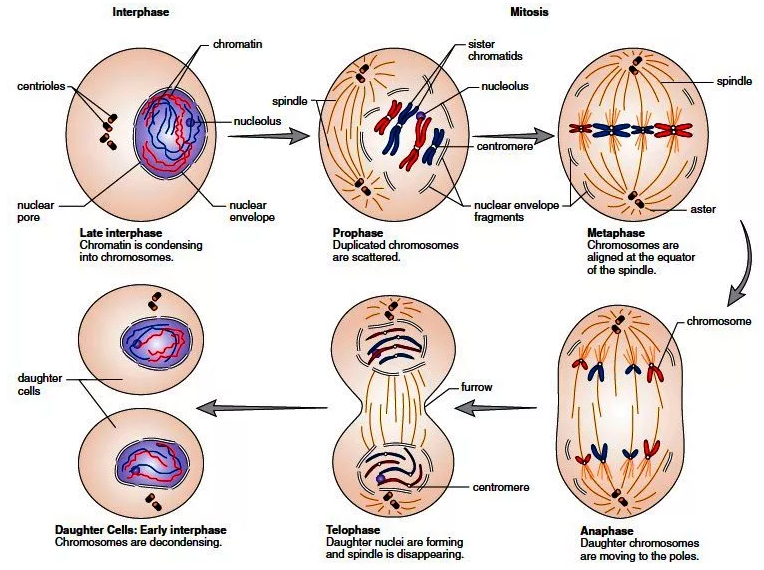
Late Interphase: Chromatine is condensing into chromosomes.
Prophase:
1. The two pairs of centrioles outside the nucleus begin moving away from each other toward opposite ends of the nucleus.
2. Spindle fibers appear between the separating centriole pairs, the nuclear envelope begins to fragment, and the nucleolus begins to disappear.
3. Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres as the chromosomes continue to shorten and thicken. During prophase, chromosomes are randomly placed in the nucleus.
Metaphase:
1. The nuclear envelope is fragmented, and the spindle occupies the region formerly occupied by the nucleus.
2. The chromosomes are now at the equator (center) of the spindle.
3. Metaphase is characterized by a fully formed spindle, and the chromosomes, each with two sister chromatids, are aligned at the equator.
Anaphase:
1. At the start of anaphase, the sister chromatids separate.
2. Once separated, the chromatids are called chromosomes. Separation of the sister chromatids ensures that each cell receives a copy of each type of chromosome and thereby has a full complement of genes.
3. During anaphase, the daughter chromosomes move to the poles of the spindle. Anaphase is characterized by the movement of chromosomes toward each pole.
Telophase:
1. Telophase begins when the chromosomes arrive at the poles.
2. During telophase, the chromosomes become indistinct chromatin again. The spindle disappears as nucleoli appear, and nuclear envelope components reassemble in each cell.
3. Telophase is characterized by the presence of two daughter nucleus.
Cytokinesis:
1. Cytokinesis is division of the cytoplasm and organelles.
2. In human cells, a slight indentation called a cleavage furrow passes around the circumference of the cell. Actin filaments form a contractile ring, and as the ring gets smaller and smaller, the cleavage furrow pinches the cell in half. As a result, each cell becomes enclosed by its own plasma membrane.
1. Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in the parent cell by half and produces four gamete cells.
2. Meiosis begins with a parent cell that is diploid, meaning it has two copies of each chromosome.
Diploid is a cell or organism that has paired chromosomes, one from each parent. In humans, cells other than human sex cells, are diploid and have 23 pairs of chromosomes. Human sex cells (egg and sperm cells) contain a single set of chromosomes and are known as haploid.